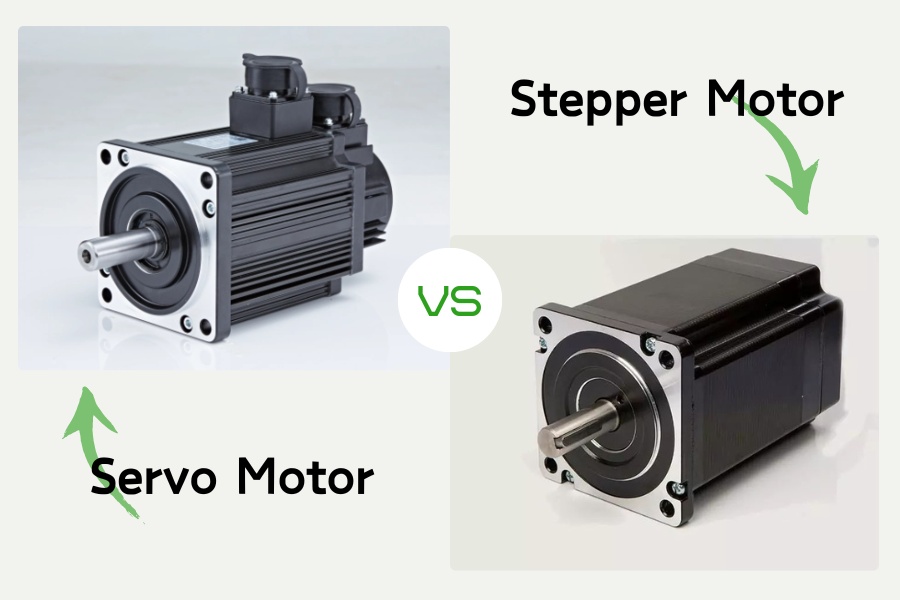
How to choose between stepper and AC servo?
15 10 月, 2020
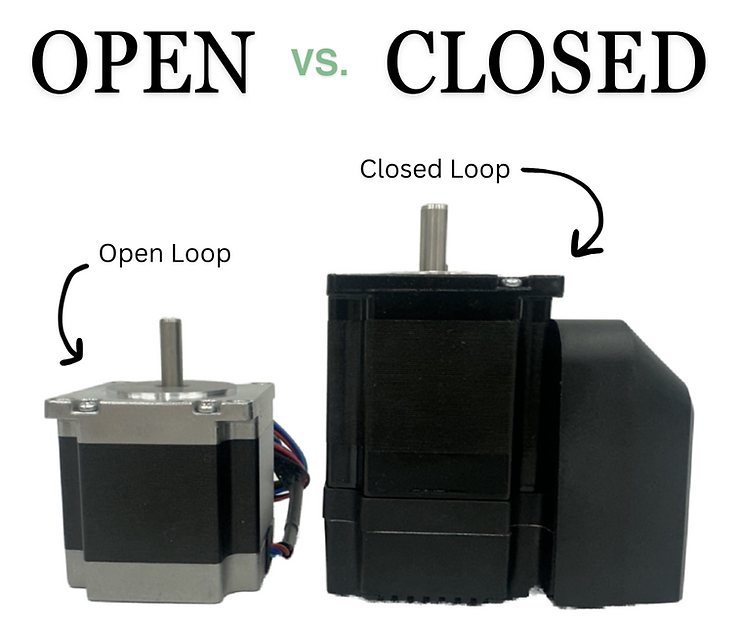
How to choose between open or close loop stepper motor and drive?
12 2 月, 2025Straight Tooth Racks vs. Helical Tooth Racks: Key Differences and Applications
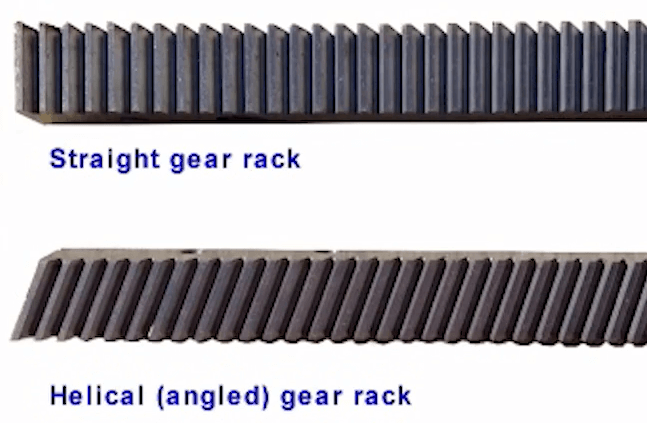
Racks are critical components in linear motion systems, converting the rotational motion of a pinion gear into linear motion. Two common types of racks are straight tooth racks and helical tooth racks, each with distinct characteristics and advantages. Understanding their differences is essential for selecting the right rack for your application.
1. Tooth Geometry
Straight Tooth Racks
Straight tooth racks feature teeth that are cut straight and parallel to the axis of the rack. This simple design makes them easy to manufacture and install. The teeth engage with the pinion gear in a straightforward manner, making them suitable for applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities.
Helical Tooth Racks
Helical tooth racks have teeth cut at an angle (helix angle) to the axis of the rack, resembling a segment of a helical gear. This angled design allows for smoother and more gradual engagement with the pinion gear. While more complex to manufacture and install, helical racks offer superior performance in high-speed and high-precision applications.
2. Performance Characteristics
Noise and Vibration
-
Straight Tooth Racks:
Straight tooth racks tend to generate more noise and vibration during operation. This is because the teeth engage abruptly, causing impact and friction. As a result, they are less suitable for applications requiring quiet operation or high speeds. -
Helical Tooth Racks:
Helical tooth racks operate more quietly and with less vibration. The angled teeth engage gradually, reducing impact and ensuring smoother motion. This makes them ideal for high-speed systems or environments where noise reduction is critical.
Load Capacity and Durability
-
Straight Tooth Racks:
Straight tooth racks have a lower load capacity because the force is concentrated on individual teeth during engagement. This can lead to faster wear and tear, especially under heavy loads or continuous operation. -
Helical Tooth Racks:
Helical tooth racks distribute the load more evenly across multiple teeth due to their angled design. This results in higher load capacity, greater durability, and longer service life, even under demanding conditions.
Efficiency and Smoothness
-
Straight Tooth Racks:
Straight tooth racks are less efficient due to higher friction and abrupt tooth engagement. They are best suited for low-to-medium speed applications where precision and smoothness are not critical. -
Helical Tooth Racks:
Helical tooth racks offer higher efficiency and smoother motion because of their gradual tooth engagement. This makes them better suited for high-speed, high-precision systems where performance and reliability are paramount.
3. Installation and Alignment
Straight Tooth Racks
Straight tooth racks are easier to install and align due to their simple tooth geometry. They do not require complex alignment procedures or additional components, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Helical Tooth Racks
Helical tooth racks require more precise alignment during installation because of their angled teeth. Additionally, they may need thrust bearings to handle the axial forces generated by the helix angle. While this increases installation complexity, the performance benefits often justify the effort.
4. Applications
Straight Tooth Racks
Straight tooth racks are commonly used in applications where simplicity and cost are more important than high performance. Examples include:
-
Conveyor systems for low-speed material handling.
-
Manual positioning stages in basic linear motion systems.
-
Low-cost automation systems with minimal precision requirements.
Helical Tooth Racks
Helical tooth racks are preferred in applications requiring high speed, precision, and smooth operation. Examples include:
-
CNC machines for high-speed cutting and milling.
-
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for smooth and quiet material handling.
-
Robotics and precision automation systems where performance is critical.
5. Key Takeaways
| Feature | Straight Tooth Racks | Helical Tooth Racks |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth Design | Straight, parallel to axis | Angled (helix angle) |
| Noise Level | Higher | Lower |
| Load Capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Installation | Easier | More complex |
| Best For | Low-speed, cost-sensitive systems | High-speed, high-precision systems |
When to Choose Which?
-
Choose Straight Tooth Racks if:
-
Your application involves low-to-medium speeds.
-
Budget constraints are a priority.
-
Simplicity and ease of installation are important.
-
-
Choose Helical Tooth Racks if:
-
High speed, precision, and smooth operation are required.
-
Noise reduction and durability are critical.
-
Your system can accommodate the additional complexity and cost.
-
Conclusion
Straight tooth racks and helical tooth racks each have their strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications. Straight tooth racks are cost-effective and easy to use, while helical tooth racks offer superior performance in demanding environments. By understanding their differences, you can make an informed decision and select the right rack for your specific needs.