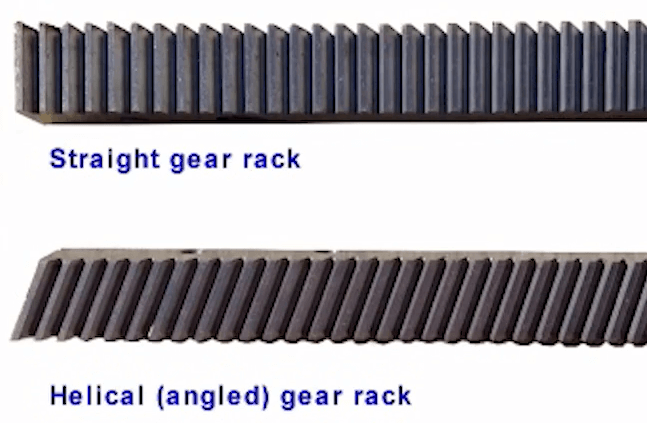
How to choose between Straight Tooth Racks and Helical Tooth Racks?
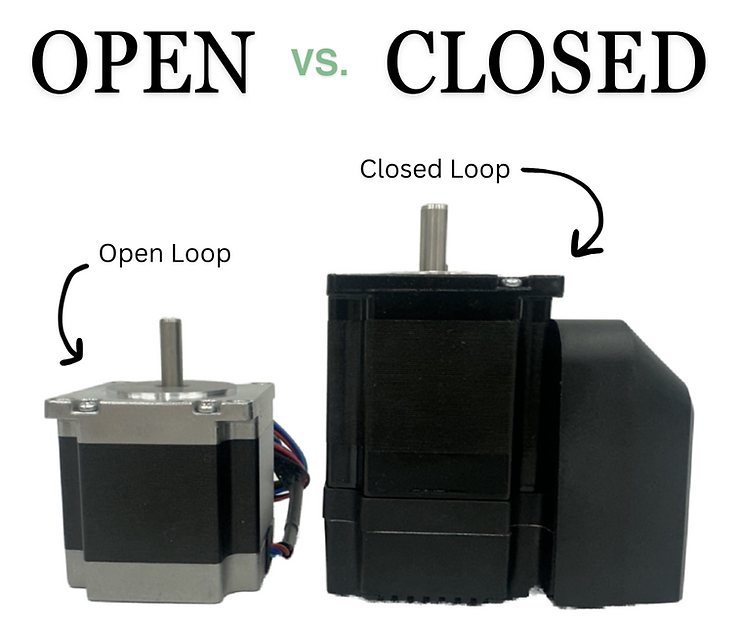
12 2 月, 2025Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Stepper Drives: Key Differences and Applications
Stepper motors are widely used in precision motion control systems, and their performance largely depends on the type of drive system used. The two primary types of stepper drives are open-loop and closed-loop systems. While both control stepper motors, they differ significantly in their operation, performance, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right drive for your needs.
1. Operating Principles
Open-Loop Stepper Drives
Open-loop stepper drives operate without feedback. The controller sends pulse signals to the motor, and the motor moves in discrete steps based on the number of pulses received. The system assumes that the motor follows the commanded steps accurately, without verifying the actual position or speed.
-
Key Characteristics:
-
No position or speed feedback.
-
Simple and cost-effective design.
-
Relies on the motor's ability to maintain step integrity.
-
Closed-Loop Stepper Drives
Closed-loop stepper drives incorporate feedback devices (e.g., encoders or resolvers) to monitor the motor's actual position and speed. The controller compares the commanded position with the feedback and adjusts the motor's operation to correct any errors.
-
Key Characteristics:
-
Uses feedback for real-time error correction.
-
More complex and expensive than open-loop systems.
-
Ensures higher accuracy and reliability.
-
2. Performance Comparison
Accuracy and Precision
-
Open-Loop Drives:
-
Prone to lost steps if the motor encounters excessive load or acceleration.
-
Accuracy depends on the motor's ability to follow the commanded steps without error.
-
Suitable for applications where occasional missed steps are acceptable.
-
-
Closed-Loop Drives:
-
Detects and corrects missed steps in real time, ensuring high accuracy.
-
Maintains precision even under varying loads or dynamic conditions.
-
Ideal for applications requiring consistent performance and reliability.
-
Torque and Speed
-
Open-Loop Drives:
-
Torque decreases significantly at higher speeds due to the motor's open-loop nature.
-
Limited by the motor's torque-speed curve, which declines as speed increases.
-
-
Closed-Loop Drives:
-
Maintains consistent torque across a wider speed range.
-
Can dynamically adjust current and voltage to optimize performance, even at high speeds.
-
Efficiency
-
Open-Loop Drives:
-
Less efficient because the motor draws full current even when not moving or under light loads.
-
Energy consumption is higher in static or low-load conditions.
-
-
Closed-Loop Drives:
-
More energy-efficient as the system adjusts current based on actual load requirements.
-
Reduces power consumption and heat generation, especially during idle or low-load periods.
-
3. System Complexity and Cost
Open-Loop Stepper Drives
-
Complexity: Simple design with no feedback components.
-
Cost: Lower upfront cost due to fewer components and simpler electronics.
-
Installation: Easier to set up and configure, making it ideal for basic applications.
Closed-Loop Stepper Drives
-
Complexity: Requires additional components, such as encoders and advanced controllers.
-
Cost: Higher initial investment due to added hardware and software complexity.
-
Installation: More challenging to set up and tune, but offers better long-term performance.
4. Applications
Open-Loop Stepper Drives
Open-loop systems are suitable for applications where cost and simplicity are more important than absolute precision. Examples include:
-
3D printers and CNC machines (for non-critical axes).
-
Conveyor systems and automated packaging machines.
-
Low-cost robotics and educational projects.
Closed-Loop Stepper Drives
Closed-loop systems excel in applications requiring high precision, reliability, and dynamic performance. Examples include:
-
High-speed CNC machines and industrial robots.
-
Medical devices and laboratory automation.
-
Advanced motion control systems with varying loads.
5. Key Takeaways
| Feature | Open-Loop Stepper Drives | Closed-Loop Stepper Drives |
|---|---|---|
| Feedback | None | Encoder or resolver feedback |
| Accuracy | Prone to lost steps | High accuracy, error correction |
| Torque at Speed | Drops significantly at high speeds | Maintains torque across speeds |
| Efficiency | Less efficient | More energy-efficient |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Best For | Low-cost, simple applications | High-precision, dynamic systems |
When to Choose Which?
-
Choose Open-Loop Stepper Drives if:
-
Your application is cost-sensitive.
-
Occasional missed steps are acceptable.
-
The system operates at low-to-medium speeds with consistent loads.
-
-
Choose Closed-Loop Stepper Drives if:
-
High precision and reliability are critical.
-
The system operates at high speeds or under varying loads.
-
Energy efficiency and dynamic performance are priorities.
-
Conclusion
Open-loop and closed-loop stepper drives serve different purposes in motion control systems. Open-loop drives are simple and cost-effective, making them ideal for basic applications. Closed-loop drives, while more complex and expensive, offer superior accuracy, efficiency, and performance, making them suitable for demanding applications. By understanding their differences, you can select the right drive system to meet your specific requirements.